Chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and obesity have become leading health concerns globally. Recent research has highlighted that these diseases often share a common underlying factor: metabolic dysfunction. The Metabolism and Medicine book delves deeply into how metabolism impacts chronic diseases and presents new approaches for addressing metabolic health to manage and even prevent these conditions.
Understanding Metabolic Dysfunction and Its Impact on Health
Metabolism, the process by which the body converts food into energy, is central to our overall health. When metabolic processes function efficiently, cells have the energy needed to perform vital functions, from muscle contraction to brain activity. However, when these processes become impaired—often due to factors like poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, or genetic predispositions—the body’s ability to regulate energy becomes compromised. This dysfunction can lead to insulin resistance, inflammation, and oxidative stress, all of which contribute to the development of chronic diseases.
In Metabolism and Medicine, the authors argue that the traditional view of treating chronic diseases by focusing on specific symptoms or organs may be inadequate. Instead, they emphasize that addressing metabolic health holistically—targeting cellular function, mitochondrial health, and nutrient metabolism—could offer more effective solutions.
Metabolic Dysfunction and Its Role in Chronic Diseases
- Diabetes and Insulin Resistance
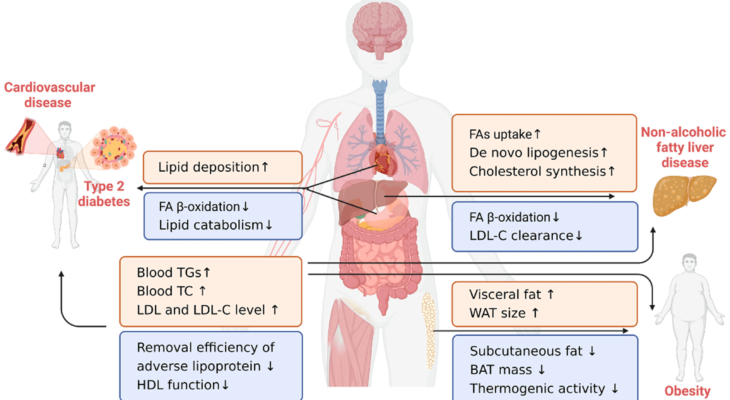
One of the most well-understood connections between metabolism and chronic disease is seen in type 2 diabetes, where the body’s ability to respond to insulin is diminished. Insulin resistance, often the precursor to diabetes, is closely linked to metabolic health. When the cells become resistant to insulin, glucose builds up in the blood, leading to high blood sugar levels and eventually diabetes. By targeting metabolic pathways and promoting cellular energy balance, Metabolism and Medicine suggests that we could prevent or even reverse insulin resistance. - Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease, which includes heart disease and stroke, is another condition linked to metabolic health. Poor lipid metabolism can lead to the buildup of cholesterol in the arteries, contributing to atherosclerosis, a major risk factor for heart disease. Additionally, chronic inflammation, a common byproduct of metabolic dysfunction, exacerbates cardiovascular risks. Metabolism and Medicine discusses the importance of managing metabolic factors like inflammation, oxidative stress, and lipid metabolism to reduce the burden of cardiovascular diseases. - Obesity and Inflammation
Obesity itself is both a result and cause of metabolic dysfunction. Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, can lead to low-grade chronic inflammation and hormonal imbalances, which further impair metabolism. This creates a cycle where inflammation and metabolic dysfunction fuel each other, increasing the risk of other chronic diseases. The book emphasizes the role of a balanced diet, physical activity, and targeted therapies that restore metabolic balance as key strategies to breaking this cycle and managing weight sustainably.
New Approaches to Metabolic Health
Metabolism and Medicine advocates for a more integrated approach to chronic disease, one that treats metabolism as the core mechanism underlying various health conditions. By focusing on the health of mitochondria—the energy-producing centers in cells—the authors suggest we can improve metabolic health on a cellular level. Nutritional interventions, physical activity, and even stress management can be tailored to support mitochondrial health, which in turn benefits the whole body.
Ultimately, the book underscores that understanding and supporting metabolism may be key to addressing the root causes of chronic diseases rather than merely treating symptoms. This shift in perspective could lead to more sustainable health outcomes and a better quality of life for individuals facing chronic conditions.